Kreditkartentransaktionen
How does a credit card transaction work?
In order for credit cards to be accepted in a webshop the following conditions must be met:
1. Contract with a Payment Service Provider (PSP)
2. Contract with an acquirer for the card acceptance of each card brand
3. Integration of the payment interface in your webshop
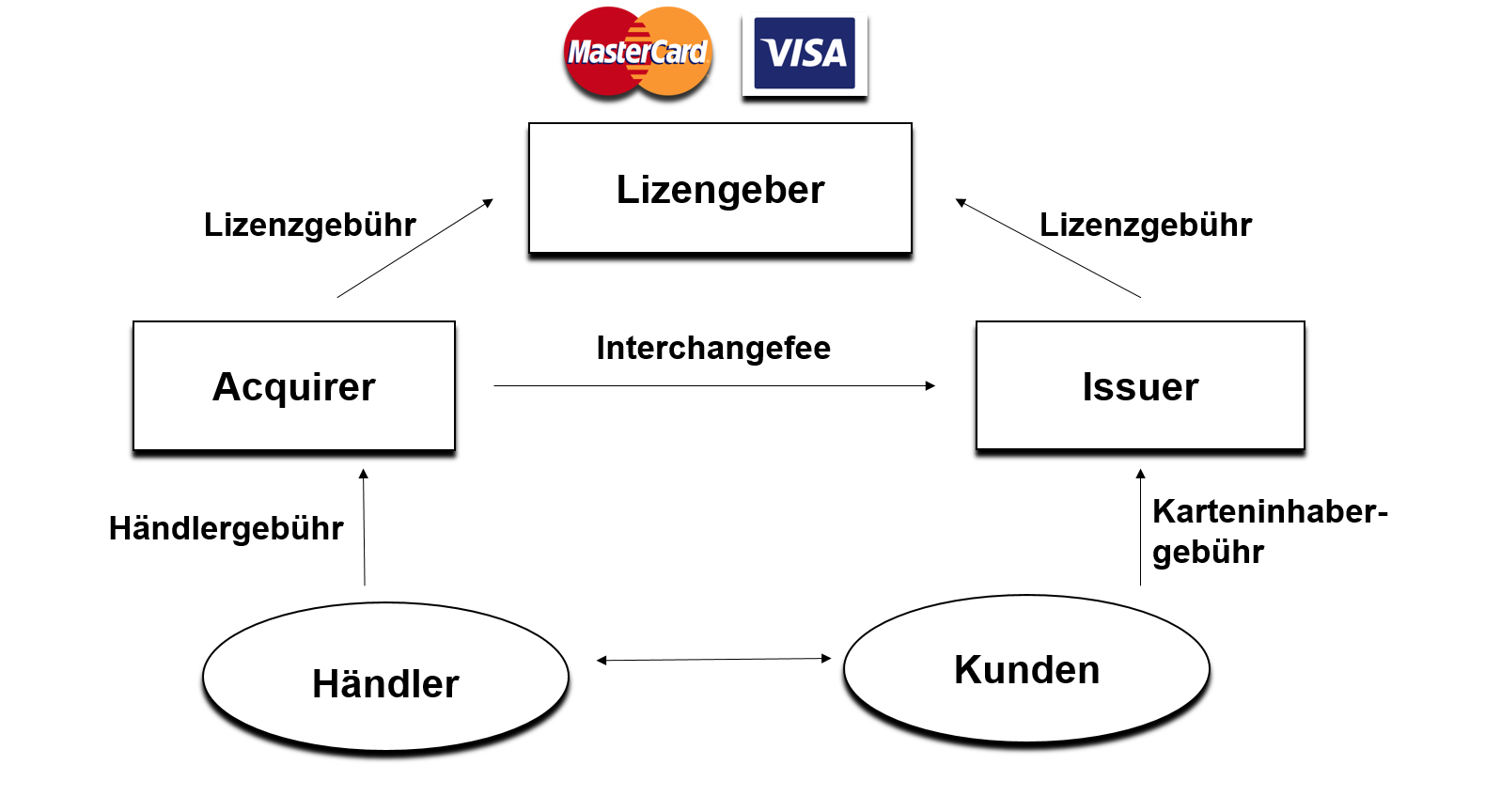
Usually five parties are involved in the process of a card transaction:
- Issuer, the bank, that issues a card to the card holder
- The card holder, who wants to complete a transaction with his card
- The Payment Service Provider, who accepts payments either on-site via terminal or on the internet via a virtual terminal
and forwards it to the Acquirer. - The contract partner (merchant), who accepts the payment by card of a product or service bought in his shop.
- Acquiring Bank / Acquirer , the bank that handles the billing of the contract partners card revenues
(Source: own presentation)
So how does a transaction in the internet work?
For a merchant to be able to offer payment via credit card one of the first things will be to decide on a Payment Service Provider (PSP) and an Aqcuiring Bank.
Payment Service Provider contracts control the different options in cashless payment methods like credit cards, PayPal, Sofort, etc. through one PSP, who for his part offers accessibility
to Aquiring Banks or other Payment Service Providers mentioned above from a single source. The PSP also verifies whether the transactions are valid and safe or if certain parameters indicate fraud.
In addition to technical hurdles and safety issues (including PCI Compliance), which are simplified by the PSP, the PSP also relieves the dealer of the massive integration effort. Without PSP, dealers would have to integrate each Payment Service Provider and Acquiring Bank individually. For his services, the PSP usually demands a transaction fee in return.
The dealer enters into a contract with his PSP directly through the credit card acceptance agreements. These are similar to a kind of credit agreement, which must be completed with a credit card bank. The Acquirers are banks which award such credit card acceptance agreements. They are members of a card network such as MasterCard or Visa. The card brands do not enter into contracts with dealers themselves. Acquirers accept credit card transactions on behalf of the dealers. In order for a transaction to be verified, the card network connects the Acquiring Bank with the Issuer.
Whenever a card holder wants to make a purchase with a credit card, the Acquiring Bank will either accept the transaction or reject it on the basis of information provided by the card network and the Issuers. Issuing and acquiring are two complementary sides of the card business.
The acquirer not only manages all transactions of cardholders, but also covers to the whole risk and assumes full responsibility in case of credit card fraud or of a card holder's insolvency or unwillingness to pay. Which is why percentage fees arise for the card holder. The merchants pay a fee to the Acquirer for each credit card transaction. This covers the costs for the administrative and IT expenses as well as the costs of authorization, cash management, payment and payment guarantee
Step by Step Process
Allow me to illustrate the process once more step by step.
As part of the checkout, the customer is prompted to enter his credit card information on the payment page of the PSP. The payment processor forwards the authorization request via Acquirer further to the issuer. If approved, the amount will be debited from the credit card holder. The issuer then sends the authorization response back to the payment processor.
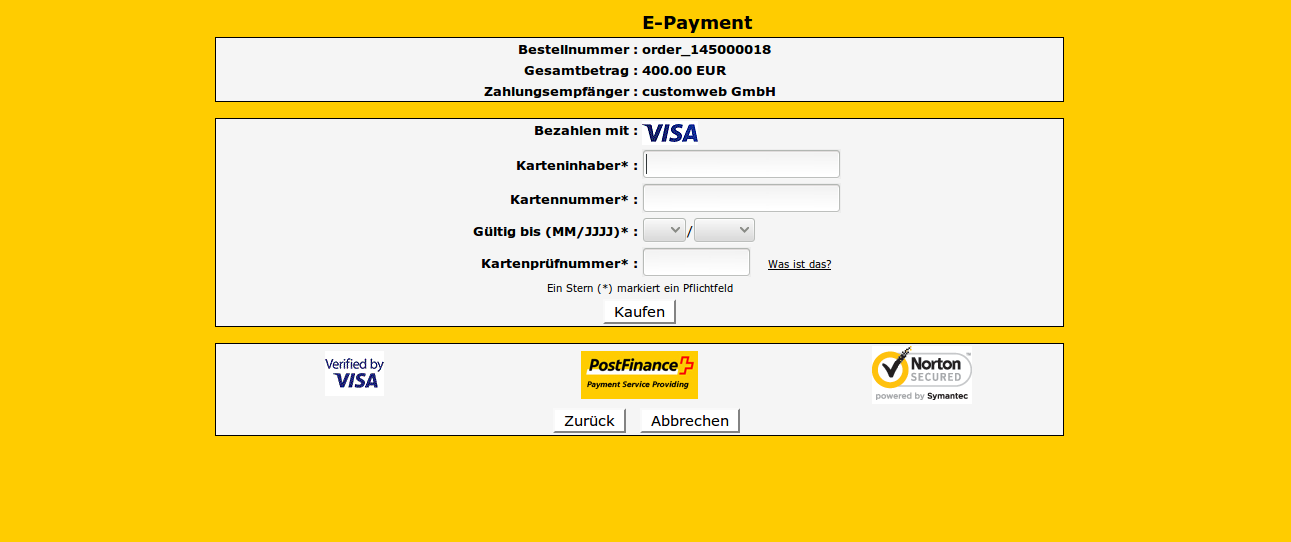
The Payment Service Provider adds response codes to the authoritative answer and sends it back to the online shop of the dealer. In the shop of the merchant, either an order will be created or the transaction will be declined - depending on the authorization response of the PSP. Below you can see an example for such a response.
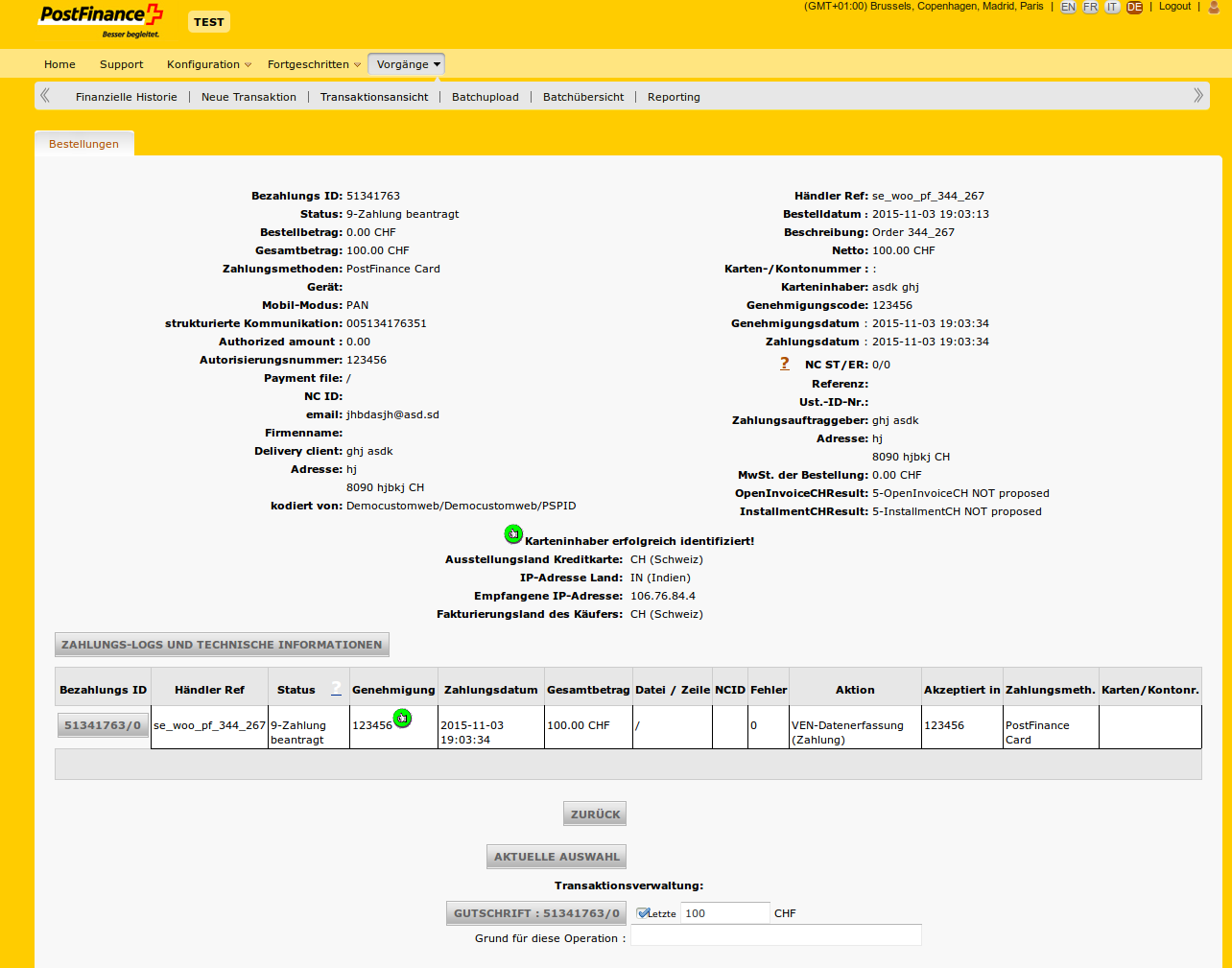
If the order was successful the merchant will deliver the goods or provide the services for the customer. The Issuer sends the corresponding amount for the transaction to the card network, which then pays them into the merchant's bank. This is called "settlement". This process typically takes two to four business days.